Income Needed to Get a Mortgage in Canada

The Bank of Canada’s recent rate adjustments have transformed housing affordability nationwide in today’s evolving economic landscape. This guide breaks down current income requirements for securing mortgage loans in various Canadian regions and cities, helping you understand how these economic shifts affect home affordability. We’ll examine critical factors like loan-to-value (LTV) ratios, debt service requirements, amortization period considerations, and the latest mortgage stress test implications for Canadian borrowers.
Key Takeaways
- Recent adjustments in Bank of Canada rates mean Canadians typically need an income of 3.5 to 4 times their mortgage amount with a 20% downpayment.
- Income requirements vary widely across provinces, with Newfoundland having the lowest required income and Vancouver having the highest.
- Your type of mortgage—whether fixed or variable rate—can significantly impact the income needed to qualify, especially with the higher stress test rates in place.
Qualifying for a Mortgage in Canada
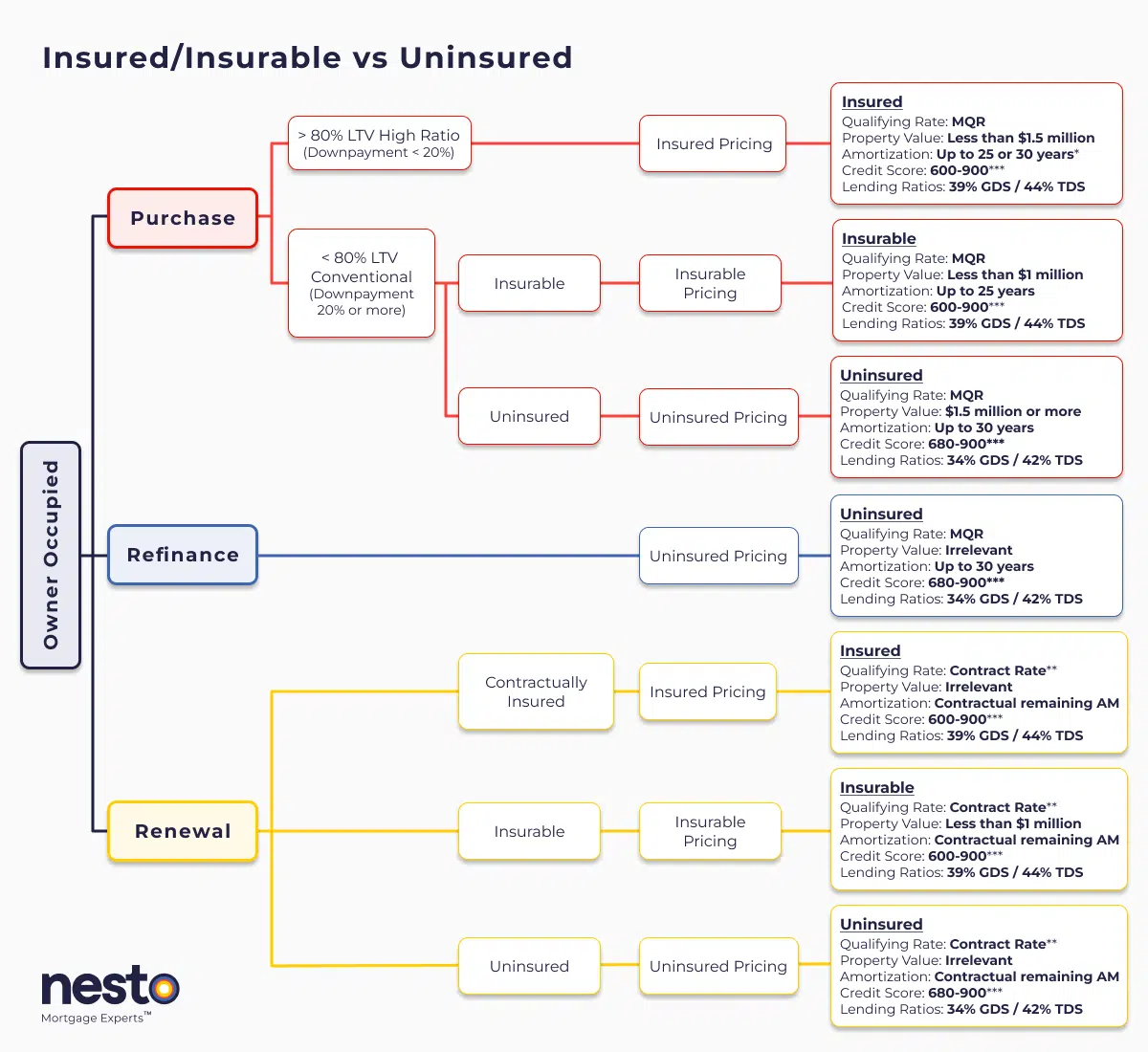
Details
*30-year amortizations on insured purchases are limited to first-time homebuyers (FTHBs) or anyone purchasing newly built homes.
**Qualified at contract rate at renewal only if there are no increases to contractually remaining amortization or remaining balance, and the mortgage is being transferred from a federally regulated lender as outlined by the Department of Finance (DOF) as a straight switch. The Minimum Qualifying Rate (MQR) requirements have been amended by the Office of the Superintendent for Financial Institutions (OSFI). It will be used to qualify all mortgages used for purchases and refinances. The MQR does not apply to renewals if the mortgage is renewed with the current lender or switched from a federally regulated lender.
***A credit score of 600 or 650 is allowable based on the mortgage insurer, and if there is a secondary applicant with a credit score of 680 or above. Lenders may scale debt service ratios (GDS/TDS) based on applicant(s) credit score(s) or reason for purchase/renewal (primary residence vs rental property). If one applicant on a joint mortgage has a credit score below 680, the lender may apply lending ratios as low as 32% GDS and 40% TDS. All criteria in the chart above apply to an owner-occupied primary residence mortgage with nesto.
Contractually insured mortgages are initially mortgage default insured by the borrower at the time of purchase and have not been refinanced or changed in any way that increases their remaining contractual amortization or mortgage balance. These insured mortgages are also known as high-ratio mortgages. In contrast, insurable and uninsured terms apply to conventional mortgages that are back-end bulk portfolio insured (typically lender-paid) or not.
New Purchase Qualifying Rates
Insured home purchases may be qualified using our lowest fixed rate, which will be the greater of 5.25% or
Insured home purchases may be qualified using our lowest variable rate, which will be the greater of 5.25% or
Insurable home purchases may be qualified using our lowest fixed rate, which will be the greater of 5.25% or
Insurable home purchases may be qualified using our lowest variable rate, which will be the greater of 5.25% or
Uninsured home purchases may be qualified using our lowest fixed rate, which will be the greater of 5.25% or
Uninsured home purchases may be qualified using our lowest variable rate, which will the greater of 5.25% or
Renewal (Switch or Transfer) Qualifying Rates
An insured mortgage may be qualified for renewal using the contract rate, which could be on our lowest fixed or variable insured rates, currently at
An insurable mortgage may be qualified for renewal using the contract rate, which could be on our lowest fixed or variable insurable rates, currently at
An uninsured mortgage may be qualified for renewal using the contract rate, which could be on our lowest fixed or variable uninsured rates, currently at
Loan-To-Value (LTV) Ratios and Qualifying Rates
Higher loan-to-value (LTV) ratios for insured mortgages remain beneficial in the current market, allowing you to access lower qualifying rates. However, higher interest rates mean borrowers must meet stricter income and credit score standards.
Understanding Debt Service Ratios
Debt service ratios, also known as debt-to-income ratios, gross debt service (GDS) and total debt service (TDS) ratios, are critical as borrowers face higher qualifying standards:
- Adjusted Ratios for Insured and Uninsured Mortgages: Insured mortgages allow up to 39% GDS and 44% TDS, while uninsured mortgages typically require lower ratios.
Focus on Financial Health: With higher interest rates, managing monthly mortgage payments within one’s financial capacity is essential.
How Do You Qualify for a Mortgage in Canada?
To qualify for a mortgage, you must pass a stress test to prove you can handle higher interest rates, which applies to all borrowers, even without mortgage default insurance. Lenders confirm you can manage your mortgage at an elevated rate, known as the minimum qualifying rate. The minimum qualifying rate (MQR) is the greater of the contracted rate plus 2% or 5.25%. However, when an insured mortgage (borrowers paid for the insurance) is transferred or switched between lenders at renewal, it will not be stress tested and is qualified at the contract rate.
Mortgage Default Insurance Requirements
Mortgage default insurance is mandatory for downpayments under 20%, impacting your mortgage qualifying amount and monthly costs. Default insurance often applies to loan amounts with higher LTV ratios, making high-ratio mortgages more affordable. Due to amortization limitations, these mortgages require a smaller downpayment despite having a higher monthly payment.
| Loan-to-Value | Premium (25-year Amortization) | Premium (30-year amortization) |
|---|---|---|
| 80.01% to 85% | 2.80% | 3.00% |
| 85.01% to 90% | 3.10% | 3.30% |
| 90.01% to 95% | 4.00% | 4.20% |
Region-Specific Income Requirements & Monthly Updates
Income requirements and purchase prices vary by location:
- Major cities like Toronto and Vancouver have higher income requirements based on property values and interest rate changes.
- Cities like Montreal are more affordable but show slight increases in required income.
Month-Over-Month Change in Income Required for Mortgages in Canadian Provinces
In some Canadian provinces, average home prices and the income required to qualify for a mortgage on an average-priced home have changed compared with last month.
Calculations are based on a mortgage with a 25-year amortization, a 20% downpayment, a provincially averaged property tax rate, and $100 for monthly heating costs. Home prices are sourced from the most recent CREA report.
Year-Over-Year Change in Income Required for Mortgages in Canadian Provinces
In some Canadian provinces, average home prices and the income required to qualify for a mortgage on an average-priced home have changed compared with last year.
Calculations are based on a mortgage with a 25-year amortization, a 20% downpayment, and a provincially averaged property tax rate, including $100 for monthly heating costs. Home prices are sourced from the most recent CREA report.
Month-Over-Month Change in Income Required for Mortgages in Canadian Cities
In some Canadian cities, average home prices and the income required to qualify for a mortgage on an average-priced home have changed compared with last month.
Calculations are based on a mortgage with a 25-year amortization, a 20% downpayment, and a provincially averaged property tax rate. They include $100 for monthly heating costs. Home prices are sourced from the most recent CREA report.
Year-Over-Year Change in Income Required for Mortgages in Canadian Cities
In some Canadian cities, average home prices and the income required to qualify for a mortgage on an average-priced home have changed compared with last year.
Calculations are based on a mortgage with a 25-year amortization, a 20% downpayment, and a provincially averaged property tax rate, including $100 for monthly heating costs. Home prices are sourced from the most recent CREA report.
Required Income for Average-Priced Homes in Canada
Based on the latest stress test requirements over a 25-year amortization, Canadians with a 20% downpayment need an income between $135,677 and $142,659 to buy Canada’s average-priced home at today’s fixed and variable rates, respectively, in November 2025.
Moreover, the income required to purchase a home in Newfoundland (at $59,970) is quite different from the income needed to buy a home in Vancouver (at $287,083).
However, an insured mortgage with a 10% downpayment and a 25-year amortization typically requires a lower income threshold than an uninsured mortgage financing due to higher uninsured mortgage rates.
Income Needed to Buy an Average-Price Home in Canada on an Insured Fixed Rate
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 10% downpayment over a 25-year amortization:
Income Needed to Buy an Average-Price Home in Canada on an Uninsured Fixed Rate
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 20% downpayment over a 30-year amortization:
How Much Do I Need to Make to Afford the Average-Priced Home in Quebec?
Compare the income required to purchase the average-priced home in Québec, as well as in some of its major cities and regions, including Montréal and Québec City.
How Much Do I Need to Make to Afford the Average-Priced Home in Ontario?
Compare the income required to purchase the average-priced home in Ontario, or in some of its major cities, such as Toronto and Mississauga.
How Much Do I Need to Make to Afford the Average-Priced Home in Alberta?
Compare the income required to purchase the average-priced home in Alberta, or in some of its major cities, such as Calgary and Edmonton.
How Much Do I Need to Make to Afford the Average-Priced Home in British Columbia?
Compare the income required to purchase the average-priced home in Alberta or some of its major cities, such as Vancouver and Victoria.
How Much Do I Need to Make to Afford the Average-Priced Home in the Prairie Provinces?
Compare the income you need to purchase the average-priced home in the Prairie provinces or some of their large cities, including Saskatoon and Winnipeg.
How Much Do I Need to Make to Afford the Average Priced Home in the Maritime Provinces?
Compare the income you need to purchase the average-priced home in the Maritime provinces or some of their large cities, including Halifax and Moncton.
What Does the Average Income Buy You Across Canada?
Income Needed to Buy an Average-Priced Home in Different Provinces
There is no simple or blanket answer to the qualifying income amount across Canada, as each municipality in every province has its own municipal property tax rate, directly affecting the income needed to qualify.
Income Needed to Buy an Average-Priced Home in Canada’s Large Cities
There is no simple or blanket answer to the qualifying income amount across Canada, as each municipality’s property tax rate directly affects the income needed to qualify.
We’re curious…
Are you a first-time buyer?
How Much Can I Get on a Different Type of Mortgage?
Income Needed to Qualify for Mortgage on Our Insured Fixed Rate
Calculations are based on a mortgage with a 25-year amortization, a 20% downpayment, and a provincially averaged property tax rate, including $100 for monthly heating costs. Home prices are sourced from the most recent CREA report.
Income Needed to Qualify for Mortgage on Our Insured Variable Rate
Calculations are based on a mortgage with a 25-year amortization, a 20% downpayment, a provincially averaged property tax rate and $100 for monthly heating costs. Home prices are sourced from the most recent CREA report.
Income Needed to Qualify for Mortgage on Our Uninsured Fixed Rate
Calculations are based on a 30-year amortization mortgage, a 20% downpayment, a provincially averaged property tax rate and $100 monthly heating costs. Home prices are sourced from the most recent CREA report.
Income Needed to Qualify for Mortgage on Our Uninsured Variable Rate
Calculations are based on a mortgage with a 25-year amortization, a 20% downpayment, a provincially averaged property tax rate, and $100 for monthly heating costs. Home prices are sourced from the most recent CREA report.
Income Needed to Qualify for Common Mortgage Balances
How Much Income Can Qualify for a $100,000 Mortgage?
How much income do you need to qualify for a $100,000 mortgage in Canada?
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 10% downpayment over a 25-year amortization:
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 20% downpayment over a 30-year amortization:
How Much Income Can Qualify for a $200,000 Mortgage?
How much income do you need to qualify for a $200,000 mortgage in Canada?
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 10% downpayment over a 25-year amortization:
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 20% downpayment over a 30-year amortization:
How Much Income Can Qualify for a $300,000 Mortgage?
How much income do you need to qualify for a $300,000 mortgage in Canada?
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 10% downpayment over a 25-year amortization:
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 20% downpayment over a 30-year amortization:
How Much Income Can Qualify for a $400,000 Mortgage?
How much income do you need to qualify for a $400,000 mortgage in Canada?
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 10% downpayment over a 25-year amortization:
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 20% downpayment over a 30-year amortization:
How Much Income Can Qualify for a $500,000 Mortgage?
How much income do you need to qualify for a $500,000 mortgage in Canada?
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 10% downpayment over a 25-year amortization:
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 20% downpayment over a 30-year amortization:
How Much Income Can Qualify for a $600,000 Mortgage?
How much income do you need to qualify for a $600,000 mortgage in Canada?
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 10% downpayment over a 25-year amortization:
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 20% downpayment over a 30-year amortization:
How Much Income Can Qualify for a $700,000 Mortgage?
How much income do you need to qualify for a $700,000 mortgage in Canada?
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 10% downpayment over a 25-year amortization:
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 20% downpayment over a 30-year amortization:
How Much Income Can Qualify for a $800,000 Mortgage?
How much income do you need to qualify for an $800,000 mortgage in Canada?
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 10% downpayment over a 25-year amortization:
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 20% downpayment over a 30-year amortization:
How Much Income Can Qualify for a $900,000 Mortgage?
How much income do you need to qualify for a $900,000 mortgage in Canada?
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 10% downpayment over a 25-year amortization does not apply on properties valued at $1 million or more:
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 20% downpayment over a 30-year amortization:
How Much Income Can Qualify for a $1,000,000 Mortgage?
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 10% downpayment over a 25-year amortization does not apply on properties valued at $1 million or more:
Qualifying on an insured rate with a 20% downpayment over a 30-year amortization:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Mortgage Affordability
What Salary Do I Need to Buy a Home in Canada Today?
Today’s mortgage income requirements depend on interest rates, purchase prices, property taxes, and heating costs. Consult a mortgage professional or a mortgage expert at nesto for personalized guidance.
Why Are Mortgage Payments Rising?
Higher interest rates mean increased monthly mortgage payments, even on new fixed-rate mortgages. Many borrowers now opt for 30-year amortizations to lower their payments to mitigate rising costs, although longer amortizations will increase total interest costs.
Why Are Variable Mortgage Payments Not Reducing?
Variable-rate mortgage (VRM) payments do not change, even as the Bank of Canada lowers policy rates. As such, when interest rates rise, more of the payment goes to the interest portion of the mortgage; when interest rates fall, more of the payment goes to the principal.
During periods of inflationary pressures when interest rates rise rapidly, VRMs may reach their trigger rate or trigger point; at this point, the payment primarily covers the unpaid interest and any ballooned or original mortgage principal due. A likely reason why many Canadians who took out VRMs in 2021 may be noticing that their payments have not reduced as quickly as expected.
By contrast, adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM) payments adjust monthly with rate changes, reducing the principal more consistently when rates fall.
How Much Income Qualifies for a $400,000 Mortgage?
To qualify for a $400,000 home loan, Canadians generally need an income between $96,038 and $100,933, factoring a 10% downpayment with today’s qualifying rates.
As of January 15, 2026, our lowest 5-year fixed mortgage rate is
Final Thoughts
Navigating Canada’s housing market, whether buying your first home or planning an upgrade, staying current on income requirements, debt service ratios, and interest rate changes will help you make confident decisions. Understanding Canada’s mortgage landscape is vital in today’s economy.
Partnering with a mortgage expert can simplify this journey—reach out to our nesto mortgage experts to explore today’s options and make the right choice for your financial future.
Why Choose nesto
At nesto, our commission-free mortgage experts, certified in multiple provinces, provide exceptional advice and service that exceeds industry standards. Our mortgage experts are salaried employees who provide impartial guidance on mortgage options tailored to your needs and are evaluated based on client satisfaction and the quality of their advice. nesto aims to transform the mortgage industry by providing honest advice and competitive rates through a 100% digital, transparent, and seamless process.
nesto is on a mission to offer a positive, empowering and transparent property financing experience – simplified from start to finish.
Contact our licensed and knowledgeable mortgage experts to find your best mortgage rate in Canada.
Ready to get started?
In just a few clicks, you can see our current rates. Then apply for your mortgage online in minutes!



